Cloud Networking Security Assessments: A Comprehensive Guide to Securing Your Cloud Infrastructure
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, ensuring the security of your cloud networks is paramount. Cloud networking security assessments play a crucial role in identifying vulnerabilities, mitigating risks, and maintaining the integrity of your cloud infrastructure. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of cloud networking security assessments, empowering you to safeguard your cloud environments effectively.
As we navigate the complexities of cloud security, this guide serves as your trusted companion, providing insights into the latest trends, best practices, and real-world examples. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or just starting your journey in cloud security, this guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge and strategies you need to protect your cloud networks.
Cloud Networking Security Assessment Overview
Cloud networking security assessments are crucial for organizations leveraging cloud computing to ensure the protection of their sensitive data and applications. These assessments identify vulnerabilities and potential threats within cloud networking environments, enabling organizations to proactively address security risks and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
There are various types of cloud networking security assessments, each with specific objectives. These include:
- Vulnerability assessments: Identify known vulnerabilities and configuration weaknesses in cloud networking components.
- Penetration testing: Simulates real-world attacks to assess the effectiveness of security controls and identify potential entry points for attackers.
- Compliance assessments: Verify adherence to industry regulations and standards, such as ISO 27001 or HIPAA.
Common cloud networking security vulnerabilities and threats include:
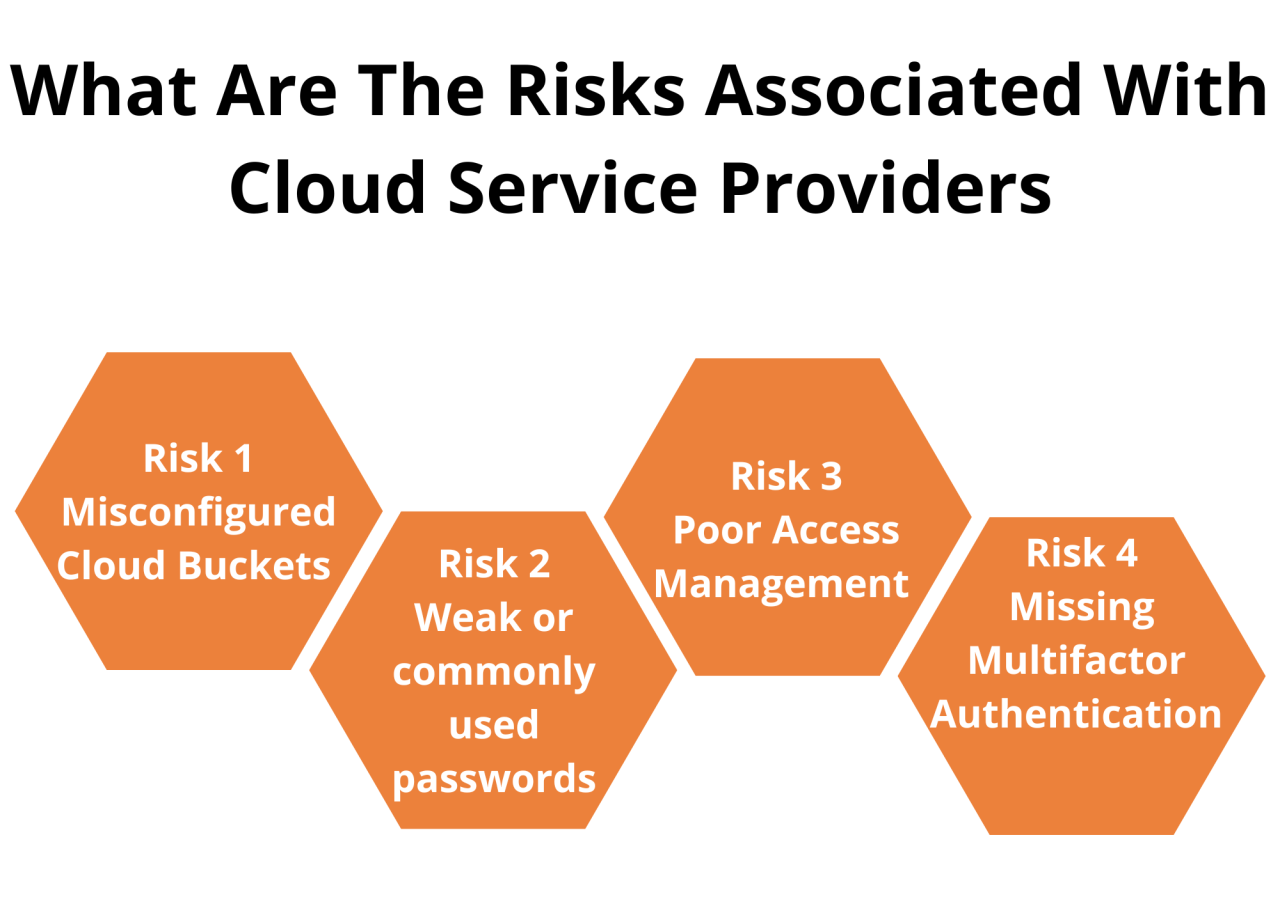
- Misconfigured security groups and network access control lists (ACLs)
- Weak or default passwords
- Unpatched software and firmware
- Insufficient logging and monitoring
- Insider threats and social engineering attacks
Conducting a cloud networking security assessment involves several key steps:
- Planning: Define the scope, objectives, and stakeholders involved in the assessment.
- Discovery: Gather information about the cloud networking environment, including its architecture, components, and security configurations.
- Assessment: Utilize appropriate tools and techniques to identify vulnerabilities and threats.
- Reporting: Document the findings, prioritize risks, and provide recommendations for remediation.
Stakeholder involvement is crucial for a successful cloud networking security assessment. This includes:
- Cloud architects and engineers
- Network administrators
- Security analysts
- Business stakeholders
Various tools and techniques can be employed to conduct cloud networking security assessments, such as:
- Vulnerability scanners
- Penetration testing tools
- Cloud-native security monitoring solutions
- Log analysis tools
Interpreting and reporting the results of a cloud networking security assessment requires a thorough understanding of the findings and their potential impact. Reports should clearly communicate the risks identified, prioritize them based on severity, and provide actionable recommendations for remediation.
Common challenges associated with conducting cloud networking security assessments include:
- Complexity and scale of cloud environments
- Rapidly evolving cloud technologies
- Lack of visibility and control over cloud resources
- Limited expertise in cloud security
Best practices for conducting cloud networking security assessments include:
- Regular assessments to keep pace with changing threats
- Use of automated tools to enhance efficiency and coverage
- Collaboration between security and IT teams
- Continuous monitoring and logging to detect and respond to threats
- Education and awareness programs for stakeholders
Cloud networking security assessments play a vital role in a comprehensive cloud security strategy. They provide organizations with a comprehensive view of their cloud networking security posture, enabling them to proactively address risks, protect their data and applications, and maintain compliance with regulations.
– the steps involved in planning and preparing for a cloud networking security assessment, including: Cloud Networking Security Assessments
Planning and preparing for a cloud networking security assessment is a critical step in ensuring the success of the assessment. By following these steps, you can ensure that you have the necessary resources and support to conduct a thorough and effective assessment.
Identifying the scope and objectives of the assessment
The first step in planning for a cloud networking security assessment is to identify the scope and objectives of the assessment. This will help you to determine the resources and expertise that you need to complete the assessment, as well as the timeline and budget for the assessment.
Identifying the key stakeholders and their roles in the assessment process
Once you have identified the scope and objectives of the assessment, you need to identify the key stakeholders who will be involved in the assessment process. This includes the individuals who will be responsible for conducting the assessment, as well as the individuals who will be responsible for reviewing and acting on the results of the assessment.
Developing a timeline and budget for the assessment
Once you have identified the key stakeholders, you need to develop a timeline and budget for the assessment. The timeline should include the start and end dates for the assessment, as well as the key milestones that need to be met during the assessment.
The budget should include the costs of the resources and expertise that you will need to complete the assessment.
Gathering necessary resources and tools
Once you have developed a timeline and budget for the assessment, you need to gather the necessary resources and tools. This includes the hardware, software, and expertise that you will need to complete the assessment.
Preparing the cloud environment for the assessment
Once you have gathered the necessary resources and tools, you need to prepare the cloud environment for the assessment. This includes configuring the cloud environment to allow for the assessment, as well as installing any necessary software or tools.
Assessment Methodology and Techniques
Cloud networking security assessments involve employing various methodologies and techniques to thoroughly evaluate the security posture of cloud networks. These approaches provide a comprehensive understanding of potential vulnerabilities and risks, enabling organizations to enhance their security measures.
The choice of assessment methodology depends on factors such as the size and complexity of the cloud network, the specific security concerns, and the resources available. Each methodology has its strengths and limitations, and selecting the most appropriate one is crucial for achieving effective results.
Vulnerability Assessment
Vulnerability assessment involves identifying and assessing known vulnerabilities in cloud network components, such as operating systems, applications, and network devices. It leverages tools and techniques to scan for security weaknesses and misconfigurations that could be exploited by attackers.
Strengths:
- Automates the process of vulnerability detection
- Provides detailed information about vulnerabilities
- Helps prioritize remediation efforts based on risk
Limitations:
- May not detect all vulnerabilities
- Can be time-consuming and resource-intensive
- Requires regular updates to stay current with emerging vulnerabilities
Penetration Testing
Penetration testing involves simulating real-world attacks to identify exploitable vulnerabilities and weaknesses in cloud networks. Ethical hackers use various techniques to gain unauthorized access to systems and data, mimicking the actions of potential attackers.
Strengths:
- Provides a comprehensive assessment of network security
- Identifies vulnerabilities that may not be detected by vulnerability assessments
- Helps organizations understand the potential impact of security breaches
Limitations:
- Can be disruptive to network operations
- Requires specialized skills and expertise
- May not be suitable for all cloud environments
Configuration Assessment
Configuration assessment evaluates the security settings and configurations of cloud network components to ensure they adhere to best practices and industry standards. It involves reviewing network configurations, firewall rules, access control lists, and other security-related settings.
Strengths:
- Identifies misconfigurations that could lead to security vulnerabilities
- Helps organizations enforce security policies and compliance requirements
- Can be automated to ensure continuous monitoring and enforcement
Limitations:
- May not detect all security vulnerabilities
- Can be time-consuming and resource-intensive
- Requires specialized knowledge of cloud network configurations
Log Analysis
Log analysis involves examining cloud network logs to identify suspicious activities, security incidents, and potential threats. It leverages advanced analytics techniques to detect patterns and anomalies that may indicate malicious behavior.
Strengths:
- Provides visibility into network activities and events
- Helps detect security incidents in real-time
- Can be used for forensic analysis and threat hunting
Limitations:
- Can be overwhelming due to the volume of logs generated
- Requires specialized skills and tools for effective analysis
- May not detect all security incidents
Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing
Vulnerability scanning and penetration testing are crucial components of cloud networking security assessments, providing valuable insights into the security posture of your cloud infrastructure. Vulnerability scanners identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations that could be exploited by attackers, while penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to assess the effectiveness of your security controls.
Vulnerability Scanners
Vulnerability scanners use automated tools to detect known vulnerabilities in your cloud environment, such as outdated software, insecure configurations, and missing security patches. These scanners compare your systems against databases of known vulnerabilities and provide detailed reports on the identified risks.
Penetration Testing Tools, Cloud networking security assessments
Penetration testing tools are used by security professionals to simulate attacks against your cloud infrastructure, identifying potential entry points and vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. These tools allow testers to probe your network for weaknesses, identify potential exploits, and assess the effectiveness of your security controls.
Interpreting and Prioritizing Vulnerability Scan Results
Vulnerability scan results can be overwhelming, so it’s important to prioritize the identified risks based on their potential impact and likelihood of exploitation. Consider factors such as the severity of the vulnerability, the ease of exploitation, and the potential impact on your business.
Focus on addressing the most critical vulnerabilities first to mitigate the highest risks.
Cloud-Specific Security Considerations
Cloud networking environments introduce unique security considerations that differ from traditional on-premises networks. These considerations stem from the inherent characteristics of cloud computing, including:
- Multi-tenancy: Cloud resources are shared among multiple tenants, each with its own security requirements.
- Shared responsibility models: Cloud providers and customers share responsibility for securing the cloud environment.
- Virtualization: Cloud resources are virtualized, which introduces additional security risks.
- Elasticity: Cloud resources can be scaled up or down on demand, which can impact security.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing: Cloud services are typically priced on a pay-as-you-go basis, which can incentivize customers to over-provision resources, increasing the attack surface.
These factors impact the effectiveness of traditional security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control lists. Cloud-specific security measures are required to address these risks, including:
- Identity and access management: Controlling who has access to cloud resources is critical.
- Data encryption: Encrypting data at rest and in transit protects it from unauthorized access.
- Vulnerability management: Regularly scanning for and patching vulnerabilities is essential.
- Incident response: Having a plan in place for responding to security incidents is crucial.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Understanding and mitigating risks associated with cloud networking environments is critical for maintaining the security and integrity of your cloud infrastructure. Risk assessment involves identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing potential threats and vulnerabilities that could impact the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your cloud-based networks.
Types of Risks in Cloud Networking
Cloud networking environments introduce unique risks that stem from shared infrastructure, multi-tenancy, and reliance on third-party providers. Common risks include:
- Data breaches:Unauthorized access to sensitive data stored or transmitted over cloud networks.
- Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks:Overwhelming cloud resources to disrupt network connectivity and services.
- Insider threats:Malicious activities by authorized users with access to cloud infrastructure.
- Configuration errors:Incorrect network configurations that create vulnerabilities or expose sensitive information.
- Cloud provider failures:Outages or security breaches within the cloud provider’s infrastructure that impact customer networks.
Risk Prioritization and Mitigation
To effectively mitigate risks, it’s essential to prioritize them based on their likelihood and potential impact. Once risks are prioritized, appropriate mitigation strategies can be implemented. Common mitigation measures include:
- Implementing strong access controls:Restricting access to cloud resources based on least privilege and multi-factor authentication.
- Monitoring and logging:Regularly monitoring network activity for suspicious behavior and logging events for audit purposes.
- Security testing:Conducting regular vulnerability scans and penetration tests to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
- Educating users:Training users on cloud security best practices and the importance of reporting suspicious activity.
- Working with cloud providers:Collaborating with cloud providers to understand their security measures and responsibilities.
By understanding the risks associated with cloud networking and implementing effective mitigation strategies, organizations can strengthen the security posture of their cloud infrastructure and protect their data and applications from potential threats.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements

Cloud networking security assessments are subject to various compliance and regulatory requirements, ensuring adherence to industry best practices and legal obligations.
Key Industry Standards and Best Practices
Compliance frameworks and industry standards provide guidelines for secure cloud networking practices. Notable examples include:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- ISO/IEC 27001:2013
- CIS Critical Security Controls
These standards define best practices for network security, including:
- Network segmentation
- Access control
- Vulnerability management
- Incident response
Ensuring Compliance
To ensure compliance with these requirements, organizations should:
- Establish a comprehensive security policy that aligns with industry standards.
- Implement technical controls and processes to enforce security measures.
- Conduct regular security assessments to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Maintain documentation and records to demonstrate compliance.
By adhering to compliance and regulatory requirements, organizations can enhance their cloud networking security posture, reduce risks, and meet legal obligations.
Reporting and Communication
Effective reporting and communication are crucial in cloud networking security assessments as they ensure that the assessment findings and recommendations are clearly and concisely conveyed to stakeholders. A comprehensive assessment report serves as a valuable resource for decision-making and risk mitigation.
The key elements of a comprehensive assessment report include:
- Executive Summary: Provides a high-level overview of the assessment findings and recommendations.
- Assessment Methodology: Describes the techniques and tools used during the assessment.
- Vulnerability Assessment Results: Details the identified vulnerabilities and their potential impact.
- Penetration Testing Results: Summarizes the results of penetration tests, including successful exploits and recommendations for remediation.
- Cloud-Specific Security Considerations: Highlights cloud-specific security concerns and provides guidance for addressing them.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Analyzes the risks associated with the identified vulnerabilities and provides recommendations for mitigation.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Addresses any applicable compliance or regulatory requirements and provides guidance for meeting them.
When communicating assessment results to stakeholders, it is essential to:
- Use clear and concise language.
- Tailor the communication to the audience’s technical expertise.
- Prioritize findings based on severity and risk.
- Provide actionable recommendations for remediation.
- Establish a regular reporting schedule to keep stakeholders informed.
– Discuss the importance of continuous monitoring and improvement in cloud networking security.
Continuous monitoring is crucial for maintaining a strong cloud networking security posture. It enables organizations to detect and respond to security threats in real-time, reducing the risk of security breaches and improving overall security posture.
Continuous monitoring involves the ongoing collection and analysis of security data from various sources, including network traffic, security logs, and cloud provider APIs. This data is used to identify potential security threats, such as unauthorized access, malware infections, and DDoS attacks.
Benefits of Continuous Monitoring
- Improved security posture: Continuous monitoring provides organizations with a comprehensive view of their cloud networking environment, enabling them to identify and address security risks in a timely manner.
- Reduced risk of security breaches: By detecting and responding to security threats in real-time, continuous monitoring can help organizations reduce the risk of security breaches and protect their sensitive data.
- Enhanced compliance: Continuous monitoring can help organizations meet compliance requirements by providing evidence of their security posture and demonstrating their commitment to data protection.
Cloud Networking Security Best Practices
Implementing Best Practices for Enhanced Cloud Networking Security
Adopting industry-leading best practices is crucial for maintaining a robust cloud networking security posture. These practices serve as a foundation for safeguarding cloud environments against cyber threats and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. By implementing these best practices, organizations can effectively protect their sensitive data, applications, and infrastructure from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other malicious activities.
Essential Security Controls and Measures
To establish a comprehensive cloud networking security framework, it is essential to implement a range of security controls and measures. These include:
- Network segmentation and isolation
- Access control and identity management
- Encryption and data protection
- Vulnerability management and patching
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems
- Security monitoring and logging
Implementation Guidance for Different Cloud Environments
The implementation of best practices and security controls may vary depending on the specific cloud environment being used. Here are some key considerations for different cloud providers:
-
-*AWS
Leverage AWS security groups, network access control lists (NACLs), and virtual private clouds (VPCs) for network segmentation and isolation. Utilize AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for access control and identity management.
-*Azure
Implement Azure Virtual Networks (VNets), network security groups (NSGs), and Azure Active Directory (AAD) for network segmentation, access control, and identity management.
-*GCP
Utilize GCP Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), firewall rules, and Identity and Access Management (IAM) for network segmentation, access control, and identity management.
Best Practices and Implementation Guidance Table
For a comprehensive overview of cloud networking security best practices, security controls, and implementation guidance, refer to the following table:| Best Practice | Security Control | Implementation Guidance ||—|—|—|| Network Segmentation | Network segmentation and isolation | Use virtual networks, subnets, and security groups to isolate different components of the network.
|| Access Control | Access control and identity management | Implement role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to restrict access to authorized users. || Encryption | Encryption and data protection | Encrypt data in transit and at rest using industry-standard encryption algorithms.
|| Vulnerability Management | Vulnerability management and patching | Regularly scan for vulnerabilities and apply patches promptly to address security risks. || Intrusion Detection | Intrusion detection and prevention systems | Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
|| Security Monitoring | Security monitoring and logging | Continuously monitor security logs and events to detect and respond to security incidents. |
Additional Resources
For further reading on cloud networking security best practices, refer to the following resources:
[AWS Security Best Practices](https
//aws.amazon.com/security/best-practices/)
[Azure Security Best Practices](https
//docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/security/fundamentals/best-practices)
[GCP Security Best Practices](https
//cloud.google.com/security/best-practices)
Emerging Trends and Technologies
The cloud networking security landscape is constantly evolving, with new trends and technologies emerging all the time. These trends are driven by the increasing adoption of cloud computing, the growing sophistication of cyberattacks, and the need for organizations to improve their security posture.
One of the most significant emerging trends in cloud networking security is the adoption of software-defined networking (SDN). SDN decouples the control plane from the data plane, which gives organizations greater flexibility and control over their networks. This flexibility can be used to improve security by implementing micro-segmentation, which isolates different parts of the network from each other.
SDN can also be used to automate security tasks, such as firewall management and intrusion detection.
Another emerging trend is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for security. AI and ML can be used to detect and respond to security threats in real time. This is important because traditional security tools are often not able to keep up with the speed and sophistication of modern cyberattacks.
Key Challenges and Opportunities
The emerging trends and technologies in cloud networking security present both challenges and opportunities for organizations. One of the biggest challenges is the need to keep up with the latest trends and technologies. This can be difficult for organizations that do not have the resources to invest in new security tools and technologies.
Another challenge is the need to integrate new security tools and technologies with existing systems. This can be a complex and time-consuming process. Organizations need to carefully plan and execute their security integrations to avoid disrupting their operations.
Despite the challenges, the emerging trends and technologies in cloud networking security also present significant opportunities for organizations. These technologies can help organizations to improve their security posture, reduce their risk of cyberattacks, and comply with regulatory requirements.
How to Prepare for and Address the Challenges
Organizations can prepare for and address the challenges of emerging trends and technologies in cloud networking security by taking the following steps:
- Educate themselves about the latest trends and technologies.
- Develop a plan for integrating new security tools and technologies with existing systems.
- Invest in training and development for their security staff.
- Partner with a managed security service provider (MSSP) to help them implement and manage their security solutions.
By taking these steps, organizations can ensure that they are prepared to address the challenges and opportunities presented by the emerging trends and technologies in cloud networking security.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Cloud networking security assessments are essential for organizations to ensure the security and compliance of their cloud environments. Several case studies and real-world examples demonstrate the value and impact of these assessments.
Key Findings and Recommendations
Common findings from cloud networking security assessments include misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and compliance gaps. Assessments typically recommend implementing security controls such as network segmentation, intrusion detection systems, and multi-factor authentication to mitigate risks.
Challenges and Trends
Organizations face challenges in conducting cloud networking security assessments, including resource constraints, lack of expertise, and rapidly evolving threats. Trends observed include the increasing adoption of cloud-native security tools and the growing importance of continuous monitoring.
Impact on Security Posture
Cloud networking security assessments have a significant impact on the security posture of organizations. By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, organizations can strengthen their defenses against cyber threats and improve their overall security posture.
Innovative Techniques and Methodologies
Assessments often leverage innovative techniques and methodologies to enhance their effectiveness. These include automated vulnerability scanning, threat intelligence analysis, and cloud-specific security frameworks.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
Case studies provide valuable lessons learned that can be applied to future assessments. These lessons include the importance of thorough planning, collaboration between security and IT teams, and continuous monitoring.
Table of Key Findings, Challenges, and Lessons Learned
| Case Study | Key Findings | Challenges | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case Study 1 | Misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, compliance gaps | Resource constraints, lack of expertise | Importance of thorough planning, collaboration |
| Case Study 2 | Security gaps in cloud-native applications | Rapidly evolving threats, cloud-specific security considerations | Need for continuous monitoring, cloud-specific security expertise |
| Case Study 3 | Effective use of cloud-native security tools | Lack of visibility into cloud environments | Value of automated vulnerability scanning, threat intelligence analysis |
Best Practices for Conducting Cloud Networking Security Assessments
- Thorough planning and preparation
- Collaboration between security and IT teams
- Leverage automated vulnerability scanning and threat intelligence analysis
- Implement cloud-specific security controls
- Establish continuous monitoring and improvement processes
Resources and Tools
To conduct effective cloud networking security assessments, a range of resources and tools are available. Understanding their strengths and limitations is crucial for selecting and using them effectively.
Cloud Security Assessment Tools
- Vulnerability Scanners:Identify known vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure and applications.
- Penetration Testing Tools:Simulate real-world attacks to identify exploitable vulnerabilities.
- Cloud Security Monitoring Solutions:Provide continuous monitoring and alerting for cloud-specific security events.
- Compliance Assessment Tools:Evaluate cloud infrastructure against industry standards and regulations.
Open Source and Commercial Tools
Both open-source and commercial tools are available for cloud networking security assessments. Open-source tools offer cost-effectiveness and customization, while commercial tools provide comprehensive features and support.
Selecting and Using Resources Effectively
- Assessment Scope:Determine the specific areas of cloud networking to be assessed.
- Tool Capabilities:Identify tools that align with the assessment objectives and target environment.
- Resource Availability:Consider the availability of skilled personnel and budget constraints.
- Integration:Ensure tools can be integrated with existing security infrastructure for efficient data analysis.
– Use a consistent style and format for defining terms.
When creating a glossary, it is important to use a consistent style and format for defining terms. This will make it easier for users to understand the terms and find the information they are looking for.
Some of the key elements to consider when defining terms include:
- Term:The term itself should be clearly stated and easy to understand.
- Definition:The definition should be clear, concise, and accurate.
- Cross-references:If the term is related to other terms in the glossary, cross-references should be included.
- Examples:Examples can help users to understand how the term is used in practice.
By following these guidelines, you can create a glossary that is easy to use and understand.
Organization
The terms in a glossary can be organized alphabetically or by category. Alphabetical order is the most common method of organization, as it makes it easy for users to find the term they are looking for. However, organizing terms by category can also be helpful, especially if the glossary is large or covers a wide range of topics.
If you choose to organize the terms by category, it is important to create a clear and logical hierarchy. The categories should be broad enough to encompass all of the terms in the glossary, but they should also be specific enough to be helpful.
Searchability
It is important to make the glossary searchable so that users can easily find the term they are looking for. One way to do this is to create an index of the terms. The index should be organized alphabetically and should include the page number where each term is defined.
Another way to make the glossary searchable is to use a search engine. Search engines can be used to search the glossary for specific terms or phrases.
Closing Notes
Embark on a journey of cloud networking security enlightenment. By embracing the guidance Artikeld in this comprehensive guide, you can proactively identify and address vulnerabilities, ensuring the resilience and integrity of your cloud infrastructure. As technology continues to advance, so too must our vigilance in safeguarding our digital assets.
Let this guide be your beacon, illuminating the path towards a secure and prosperous cloud networking future.