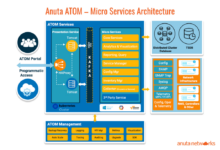
Cloud Networking with 5G Integration: A Revolutionary Convergence
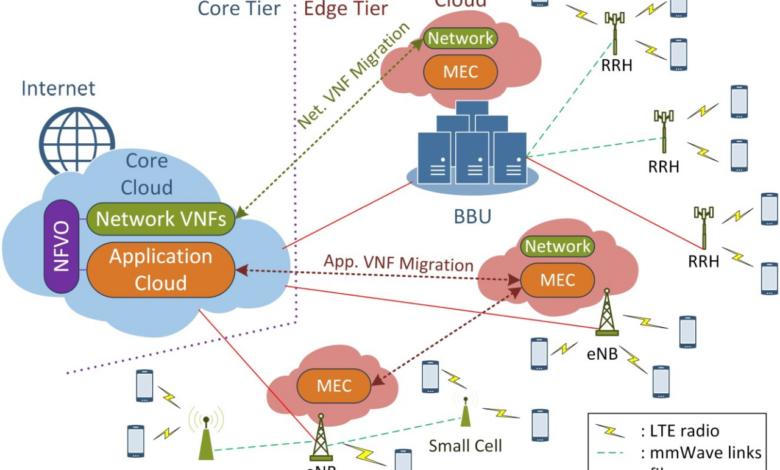
Cloud networking with 5G integration is revolutionizing the way we connect, unlocking unprecedented possibilities for businesses and consumers alike. By seamlessly blending the agility and scalability of cloud computing with the ultra-fast speeds and low latency of 5G, this transformative technology is paving the way for a future of seamless connectivity, enhanced user experiences, and groundbreaking applications.
As we delve into this captivating topic, we will explore the key components, benefits, and use cases of cloud networking with 5G integration. We will also discuss the challenges and opportunities presented by this convergence, providing insights and best practices to help organizations harness its full potential.
Cloud Network Architecture with 5G Integration
Cloud network architecture integrated with 5G technology is a combination of cloud computing and 5G networks. It provides a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective way to manage and deliver network services. The key components of a cloud network architecture with 5G integration include:
- Cloud computing platform:This provides the infrastructure and services needed to run network functions, such as virtualized network functions (VNFs) and software-defined networking (SDN) controllers.
- 5G network:This provides the high-speed, low-latency connectivity needed to support mobile applications and services.
- Network management system:This manages and orchestrates the network resources, including the cloud computing platform and the 5G network.
Integrating 5G with cloud networking offers several benefits, including:
- Increased flexibility:Cloud networking allows network operators to quickly and easily provision and manage network resources, which can help them to meet the changing needs of their customers.
- Improved scalability:Cloud networking can be scaled up or down to meet the changing demands of traffic, which can help to improve the performance of network applications and services.
- Reduced costs:Cloud networking can help to reduce the costs of network operations, as it eliminates the need for expensive hardware and software.
Cloud networking with 5G integration can be used in a variety of industries, including:
- Telecommunications:Cloud networking can be used to provide a variety of telecommunications services, such as voice, data, and video.
- Healthcare:Cloud networking can be used to provide a variety of healthcare services, such as telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, and electronic health records.
- Transportation:Cloud networking can be used to provide a variety of transportation services, such as connected vehicles, traffic management, and smart parking.
Network Slicing and 5G Integration
Network slicing is a key technology for 5G networks. It allows network operators to create multiple virtual networks on a single physical network infrastructure. This enables them to provide different levels of service to different types of applications and users.
Benefits of Network Slicing for Cloud Networking
Network slicing offers several benefits for cloud networking, including:
- Improved performance:Network slicing can be used to create dedicated network slices for cloud applications, which can improve performance by reducing latency and jitter.
- Increased security:Network slicing can be used to isolate cloud applications from each other, which can improve security by reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Greater flexibility:Network slicing allows network operators to quickly and easily create new network slices to meet the changing needs of cloud applications.
Examples of Network Slicing Use Cases
Network slicing can be used to improve cloud network performance in a variety of ways. For example, it can be used to:
- Create dedicated network slices for latency-sensitive applications, such as online gaming and video streaming.
- Create dedicated network slices for security-sensitive applications, such as financial transactions and healthcare data.
- Create dedicated network slices for high-bandwidth applications, such as cloud storage and data analytics.
Role of SDN and NFV in Network Slicing
Software-defined networking (SDN) and network functions virtualization (NFV) are key technologies that enable network slicing. SDN allows network operators to programmatically control the network, while NFV allows them to virtualize network functions.
SDN and NFV together enable network operators to create and manage network slices in a flexible and automated way.
Challenges and Limitations of Network Slicing
While network slicing offers several benefits, there are also some challenges and limitations to consider. These include:
- Complexity:Network slicing can be complex to implement and manage.
- Cost:Network slicing can be expensive to implement.
- Interoperability:Network slicing is not yet fully standardized, which can make it difficult to interoperate between different vendors’ equipment.
Edge Computing and 5G Integration
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage resources closer to the devices and users that need them. This can significantly reduce latency and improve performance for applications that require real-time data processing, such as autonomous vehicles, virtual reality, and augmented reality.Integrating
edge computing with cloud networking can provide several benefits, including:
- Reduced latency: Edge computing can reduce latency by bringing computation and data storage closer to the devices and users that need them. This can be critical for applications that require real-time data processing, such as autonomous vehicles, virtual reality, and augmented reality.
- Improved performance: Edge computing can improve performance by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network. This can be especially beneficial for applications that require large amounts of data, such as video streaming and video conferencing.
- Increased reliability: Edge computing can increase reliability by providing a backup for cloud services. If the cloud is unavailable, edge devices can continue to provide services to users.
- Reduced costs: Edge computing can reduce costs by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network. This can lead to savings on bandwidth costs.
Use Cases
There are many potential use cases for edge computing in cloud networking. Some examples include:
- Autonomous vehicles: Edge computing can be used to process data from sensors on autonomous vehicles in real time. This can help the vehicles to make decisions about their surroundings and avoid accidents.
- Virtual reality: Edge computing can be used to process data from virtual reality headsets in real time. This can help to create a more immersive and realistic experience for users.
- Augmented reality: Edge computing can be used to process data from augmented reality headsets in real time. This can help to overlay digital information onto the real world, providing users with a more informative and interactive experience.
Security Considerations for Cloud Networking with 5G Integration
Cloud networking with 5G integration introduces a new set of security challenges that must be addressed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and services.
One of the primary security challenges is the increased attack surface that is created by the integration of 5G networks with cloud networks. 5G networks are more complex than traditional cellular networks, and they introduce new vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers.
Best Practices for Securing Cloud Networks Integrated with 5G
- Implement strong authentication and authorization mechanisms to control access to cloud networks and 5G infrastructure.
- Use encryption to protect data in transit and at rest.
- Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor for suspicious activity and block attacks.
- Regularly patch and update software to fix security vulnerabilities.
- Educate users about security best practices and train them to recognize and report suspicious activity.
Security Measures to Protect Cloud Networks from Threats
There are a number of security measures that can be implemented to protect cloud networks from threats, including:
- Firewalls: Firewalls can be used to block unauthorized access to cloud networks.
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems: Intrusion detection and prevention systems can be used to detect and block malicious traffic.
- Virtual private networks (VPNs): VPNs can be used to create secure tunnels between cloud networks and on-premises networks.
- Data encryption: Data encryption can be used to protect data from unauthorized access.
- Access control lists (ACLs): ACLs can be used to control who has access to cloud resources.
Latency and Performance Optimization in Cloud Networking with 5G Integration
Latency and performance optimization are critical for cloud networking with 5G integration to deliver seamless user experiences. 5G networks promise ultra-low latency and high bandwidth, enabling real-time applications and services. However, integrating 5G with cloud networks introduces challenges in managing latency and ensuring optimal performance.
Techniques for Latency and Performance Optimization
To optimize latency and performance in cloud networks integrated with 5G, several techniques can be employed:
-
-*Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
NFV decouples network functions from hardware, allowing them to run on virtualized platforms. This enables dynamic scaling and placement of network functions to optimize performance and reduce latency.
-*Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
SDN provides centralized control over the network infrastructure, enabling flexible configuration and optimization of network resources. SDN can be used to prioritize traffic, implement load balancing, and minimize latency.
-*Edge Computing
Edge computing brings compute and storage resources closer to the network edge, reducing latency for latency-sensitive applications. By processing data locally, edge computing minimizes the distance data must travel, resulting in improved performance.
-*Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC)
MEC is a specialized form of edge computing that supports mobile applications. MEC provides ultra-low latency and high bandwidth for mobile devices, enabling real-time services and applications.
Examples of Latency and Performance Optimization
In practice, latency and performance optimization in cloud networks with 5G integration have been achieved through various applications:
-
-*Cloud Gaming
Cloud gaming services require ultra-low latency to deliver a seamless gaming experience. By integrating 5G with cloud gaming platforms, latency can be significantly reduced, allowing gamers to enjoy high-quality gaming experiences remotely.
- *Virtual Reality (VR) and
-*Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR applications demand high bandwidth and low latency to provide immersive experiences. Cloud networking with 5G integration can meet these requirements, enabling the delivery of VR and AR content with minimal lag and buffering.
-*Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles rely on real-time data processing and communication for safe and efficient operation. 5G integration with cloud networks can provide the necessary low latency and high bandwidth to support autonomous vehicle communication and data processing.
Scalability and Flexibility in Cloud Networking with 5G Integration
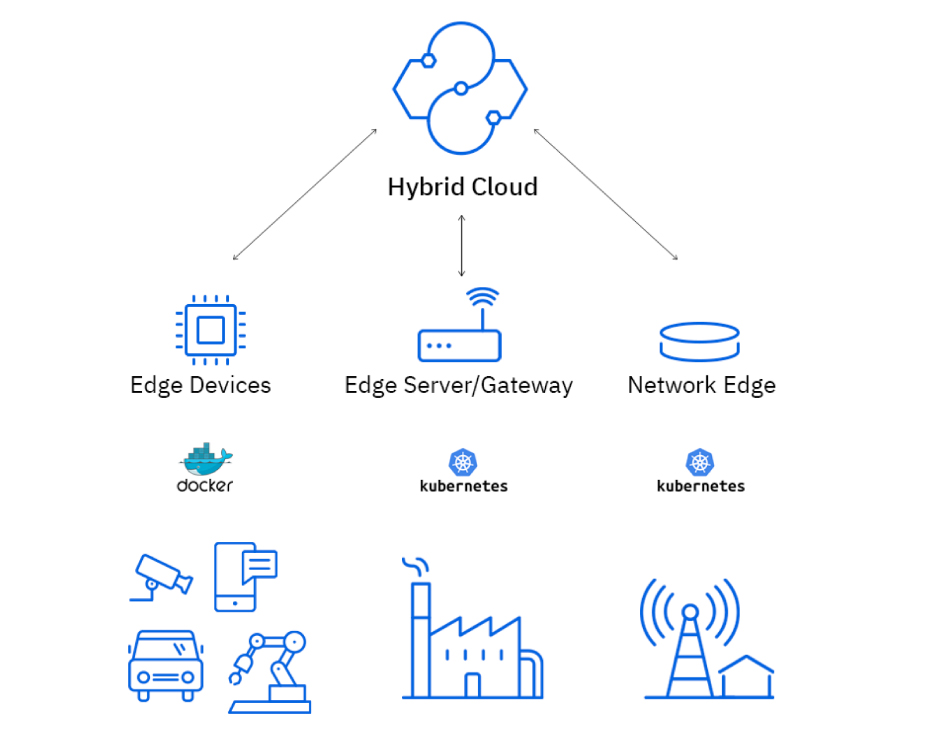
In cloud networking with 5G integration, scalability and flexibility are critical for accommodating the dynamic and demanding requirements of 5G networks. Scalability refers to the ability of the network to handle increasing traffic and network capacity, while flexibility allows the network to adapt to changing network conditions and service requirements.
Techniques for achieving scalability and flexibility in cloud networks integrated with 5G include:
Scalability and Flexibility Techniques
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Network Function Virtualization (NFV) | – Decouples network functions from hardware
|
– Can introduce latency and performance overhead |
| Software-Defined Networking (SDN) | – Centralized control and management of network resources
|
– Requires significant changes to existing network infrastructure |
| Cloud-Native Network Functions (CNFs) | – Designed specifically for cloud environments
|
– May not support all legacy network functions |
For example, a telecommunications company implemented a cloud-native 5G core network using CNFs and SDN. This solution enabled the company to scale its network capacity dynamically to meet the increasing demand for 5G services while also providing the flexibility to adapt to changing network conditions and service requirements.
Cost Optimization in Cloud Networking with 5G Integration
Cost optimization is paramount in cloud networking with 5G integration to ensure efficient resource utilization and financial sustainability. By adopting cost-effective strategies, organizations can maximize the benefits of cloud and 5G technologies while minimizing operational expenses.
Optimizing Network Architecture
Optimizing network architecture involves designing a network infrastructure that meets performance requirements while minimizing costs. This can be achieved through:
- Consolidating network resources
- Virtualizing network functions
- Leveraging cloud-native networking services
Automating Network Management
Automating network management tasks can significantly reduce operational costs. Automation tools can:
- Configure and manage network devices
- Monitor network performance
- Identify and resolve network issues
Leveraging 5G Network Slicing
5G network slicing allows organizations to create isolated virtual networks tailored to specific applications or services. This enables cost optimization by:
- Allocating resources efficiently
- Optimizing network performance for specific workloads
- Reducing the need for dedicated hardware
Case Study: Cost Reduction through Network Optimization
A leading cloud provider implemented network optimization techniques and reduced its networking costs by 30%. By consolidating network resources, virtualizing network functions, and automating network management, the provider significantly reduced its hardware and operational expenses.
Potential Cost Savings and ROI
Implementing cost optimization techniques in cloud networks with 5G integration can result in substantial cost savings and ROI. Organizations can expect to:
- Reduce hardware costs
- Lower operational expenses
- Improve network efficiency
Recommendations for Cost Optimization
Organizations can implement cost optimization strategies by:
- Conducting a thorough network assessment
- Adopting cloud-native networking services
- Automating network management
- Leveraging 5G network slicing
- Continuously monitoring and optimizing network performance
Use Cases and Applications of Cloud Networking with 5G Integration
Cloud networking with 5G integration has opened up a wide range of possibilities for businesses and organizations across various industries. By leveraging the high speed, low latency, and increased bandwidth of 5G networks, cloud networking solutions can provide enhanced connectivity, flexibility, and scalability.
- Improved Connectivity:Cloud networking with 5G integration allows for seamless and reliable connectivity between devices, applications, and cloud services, regardless of their location. This improved connectivity enables real-time data transfer and supports applications that require high bandwidth, such as video streaming, virtual reality, and augmented reality.
- Enhanced Flexibility:Cloud networking with 5G integration provides businesses with greater flexibility in managing their network infrastructure. By leveraging cloud-based services, organizations can quickly provision and scale their networks to meet changing business needs, without the need for expensive hardware upgrades or complex configurations.
- Increased Scalability:Cloud networking with 5G integration offers scalability to support the growing demands of connected devices and applications. The elastic nature of cloud computing allows businesses to easily scale their networks up or down, based on their requirements, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- Reduced Costs:Cloud networking with 5G integration can help businesses reduce their IT infrastructure costs. By leveraging cloud-based services, organizations can eliminate the need for costly hardware purchases, maintenance, and upgrades. Additionally, cloud providers offer flexible pricing models that allow businesses to pay only for the resources they consume.
- Improved Security:Cloud networking with 5G integration can enhance network security by leveraging cloud-based security services. These services provide advanced protection against cyber threats, such as malware, phishing, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
Benefits and Challenges of Using Cloud Networking with 5G Integration in Different Applications
The benefits of using cloud networking with 5G integration vary depending on the specific application. However, some common benefits include:
- Reduced latency:5G networks offer significantly lower latency than traditional cellular networks, which is crucial for applications that require real-time data processing, such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and virtual reality.
- Increased bandwidth:5G networks provide higher bandwidth than previous cellular generations, enabling faster data transfer and supporting bandwidth-intensive applications, such as video streaming, cloud gaming, and augmented reality.
- Improved reliability:5G networks are designed to be more reliable than previous cellular generations, providing a stable and consistent connection for mission-critical applications, such as remote patient monitoring, public safety, and industrial automation.
Examples of Cloud Networking with 5G Integration in Different Industries
Cloud networking with 5G integration is being used in a variety of industries to enhance connectivity, flexibility, and scalability. Some examples include:
- Healthcare:Cloud networking with 5G integration is enabling remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and precision medicine. By leveraging the high speed and low latency of 5G networks, healthcare providers can access real-time patient data, provide remote consultations, and deliver personalized treatments.
- Manufacturing:Cloud networking with 5G integration is supporting smart factories and industrial automation. By connecting sensors, robots, and other equipment to the cloud, manufacturers can monitor and control production processes remotely, optimize supply chains, and improve efficiency.
- Transportation:Cloud networking with 5G integration is powering connected vehicles and autonomous driving. By leveraging the low latency and high bandwidth of 5G networks, vehicles can communicate with each other and with roadside infrastructure, enabling real-time traffic management, accident prevention, and enhanced passenger safety.
- Retail:Cloud networking with 5G integration is enhancing customer experiences in retail stores. By providing seamless connectivity and personalized shopping experiences, retailers can attract and retain customers, increase sales, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Networking with 5G Integration
The convergence of cloud networking and 5G technology is driving the emergence of new trends that are reshaping the future of connectivity. These trends include:
- Network slicing:Network slicing allows multiple virtual networks to be created on a single physical network infrastructure, enabling service providers to offer tailored services to different types of customers.
- Edge computing:Edge computing brings cloud computing capabilities closer to the end user, reducing latency and improving performance for applications that require real-time data processing.
- Software-defined networking (SDN):SDN decouples the control plane from the data plane, enabling network administrators to programmatically manage and configure networks.
- Network function virtualization (NFV):NFV virtualizes network functions, such as firewalls and load balancers, making them more flexible and scalable.
- Artificial intelligence (AI):AI is being used to automate network management tasks, optimize network performance, and detect and mitigate security threats.
These trends are having a profound impact on the future of cloud networking. They are enabling the development of new and innovative applications, such as:
- Self-driving cars:Self-driving cars require real-time data processing to make decisions about how to navigate the road. Edge computing and 5G can provide the low latency and high bandwidth needed to support these applications.
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR):VR and AR applications require high bandwidth and low latency to deliver immersive experiences. 5G and edge computing can provide the necessary performance for these applications.
- Smart cities:Smart cities use sensors and IoT devices to collect data about traffic, pollution, and other factors. 5G and edge computing can provide the connectivity and processing power needed to support these applications.
The emerging trends in cloud networking with 5G integration are creating a new era of connectivity that is faster, more flexible, and more secure. These trends are enabling the development of new and innovative applications that will change the way we live and work.
Challenges and Limitations of Cloud Networking with 5G Integration
Cloud networking with 5G integration brings forth a myriad of opportunities but also poses certain challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for successful implementation. These include technical complexities, security concerns, latency issues, scalability limitations, and cost considerations. Understanding and overcoming these challenges are crucial for realizing the full potential of cloud networking with 5G integration.
Technical Complexities
Integrating cloud networking with 5G networks introduces a new level of complexity due to the different architectures and protocols involved. Network slicing, edge computing, and virtualization technologies must be carefully orchestrated to ensure seamless interoperability and efficient resource utilization. This complexity can make it challenging to manage and troubleshoot the integrated network, requiring specialized expertise and tools.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations for Cloud Networking with 5G Integration
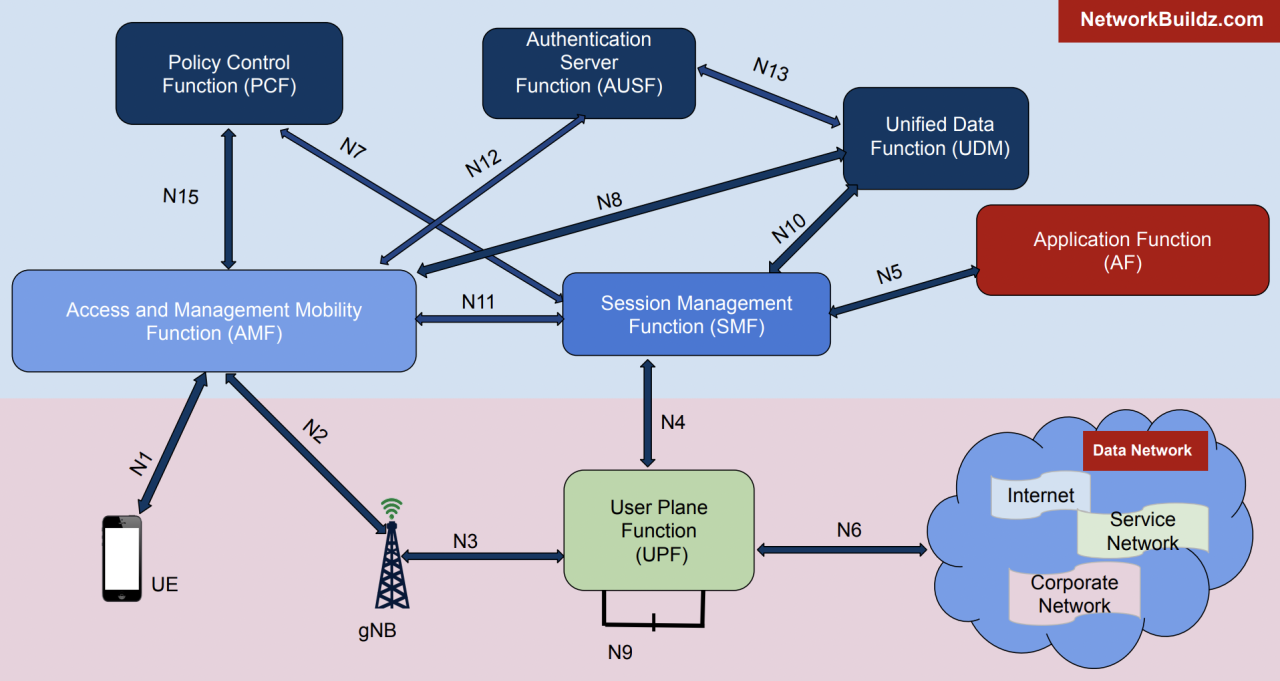
The convergence of cloud networking and 5G technology brings forth a complex regulatory and compliance landscape that requires careful consideration. This section delves into the key regulatory and compliance aspects associated with cloud networking with 5G integration, exploring their impact and providing guidance on how to address them effectively.
Impact of Regulations and Compliance
Regulations and compliance play a crucial role in shaping the deployment and operation of cloud networks integrated with 5G. They establish legal frameworks that govern the use of spectrum, data protection, privacy, and network security, among other aspects. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in significant penalties, reputational damage, and service disruptions.
Regulatory Bodies and Compliance Requirements
The regulatory landscape for cloud networking with 5G integration varies across different regions and jurisdictions. Key regulatory bodies include the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States, the European Commission (EC) in the European Union, and the Communications Authority of Kenya (CAK) in Kenya.
These bodies enforce regulations related to spectrum allocation, data privacy, network security, and competition.
Addressing Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
To ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, organizations should adopt a proactive approach. This involves:
- Identifying applicable regulations and compliance requirements
- Implementing technical and operational measures to meet regulatory standards
- Establishing clear policies and procedures for data handling and network security
- Engaging with regulatory bodies and industry associations to stay abreast of regulatory changes
Best Practices and Case Studies
Best practices for addressing regulatory and compliance considerations include:
- Leveraging cloud-based compliance solutions
- Partnering with managed service providers with expertise in regulatory compliance
- Participating in industry working groups and forums
Case studies demonstrating successful approaches to regulatory compliance include:
- AT&T’s collaboration with IBM to develop a cloud-based compliance platform
- Vodafone’s partnership with Microsoft to enhance data privacy and security
Best Practices for Cloud Networking with 5G Integration
Cloud networking with 5G integration offers immense benefits, but to harness its full potential, it’s crucial to adhere to established best practices. These practices ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and security in your cloud-integrated 5G network.
By implementing these best practices, you can:
- Maximize network performance and reliability
- Enhance security and reduce risks
- Optimize cost-efficiency
- Future-proof your network for evolving demands
Network Design and Architecture
Plan and design your cloud network architecture with 5G integration in mind. Consider the specific requirements of your applications and services, and select the appropriate network topology and components to support them. A well-designed architecture will ensure efficient traffic flow and minimize latency.
Network Segmentation and Isolation
Segment your network into logical subnets to isolate different types of traffic and enhance security. This practice helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and ensures the availability and performance of critical applications.
Security Considerations
Implement robust security measures to protect your cloud-integrated 5G network from cyber threats. Utilize encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security controls to safeguard data and prevent unauthorized access.
Performance Optimization
Continuously monitor and optimize network performance to ensure low latency and high throughput. Use performance monitoring tools to identify bottlenecks and implement appropriate measures to improve network efficiency.
Scalability and Flexibility
Design your cloud network with scalability and flexibility in mind. Choose cloud services that can easily scale up or down to meet changing demands. This will ensure your network can adapt to evolving business needs and traffic patterns.
Cost Optimization
Utilize cloud-based pricing models and cost optimization tools to manage network expenses effectively. Consider using on-demand pricing or spot instances to reduce costs without compromising performance.
Use Case Considerations
Identify the specific use cases and applications that will benefit most from cloud networking with 5G integration. This will help you prioritize investments and ensure that your network is optimized for the services you need.
Vendor Selection, Cloud networking with 5G integration
Choose cloud and 5G network providers with proven expertise and a strong track record of delivering reliable and secure services. Consider their technical capabilities, customer support, and pricing models to ensure a successful partnership.
Future Research Directions in Cloud Networking with 5G Integration
Cloud networking with 5G integration is a rapidly evolving field, and there are many exciting research directions that are being pursued. These research directions have the potential to significantly impact the future of cloud networking, making it more efficient, reliable, and secure.One
of the most important research directions is the development of new network architectures that can support the unique requirements of 5G networks. These architectures will need to be able to handle the high data rates, low latency, and high reliability that are required for 5G applications.Another
important research direction is the development of new network management and orchestration tools that can manage the complexity of 5G networks. These tools will need to be able to automate tasks such as network provisioning, configuration, and optimization.In addition, there is a need for research on new security technologies that can protect 5G networks from cyberattacks.
These technologies will need to be able to detect and mitigate threats in real-time.Finally, there is a need for research on new ways to optimize the performance of cloud networking with 5G integration. This research will need to focus on improving latency, throughput, and reliability.The
following table summarizes the key research directions in cloud networking with 5G integration, their potential impact, and examples of ongoing research:| Research Direction | Potential Impact | Examples of Ongoing Research ||—|—|—|| New network architectures | Improved performance, reliability, and security | OpenAirInterface, srsLTE || New network management and orchestration tools | Reduced complexity and improved efficiency | Open Network Automation Platform, ONAP || New security technologies | Enhanced security | 5G Security Alliance, 3GPP || Performance optimization | Improved latency, throughput, and reliability | SDN, NFV |The future of cloud networking with 5G integration is bright.
The research directions that are being pursued have the potential to significantly improve the performance, reliability, and security of 5G networks. This will enable new applications and services that will benefit businesses and consumers alike.
Comparative Analysis of Cloud Networking with 5G Integration vs. Traditional Networking
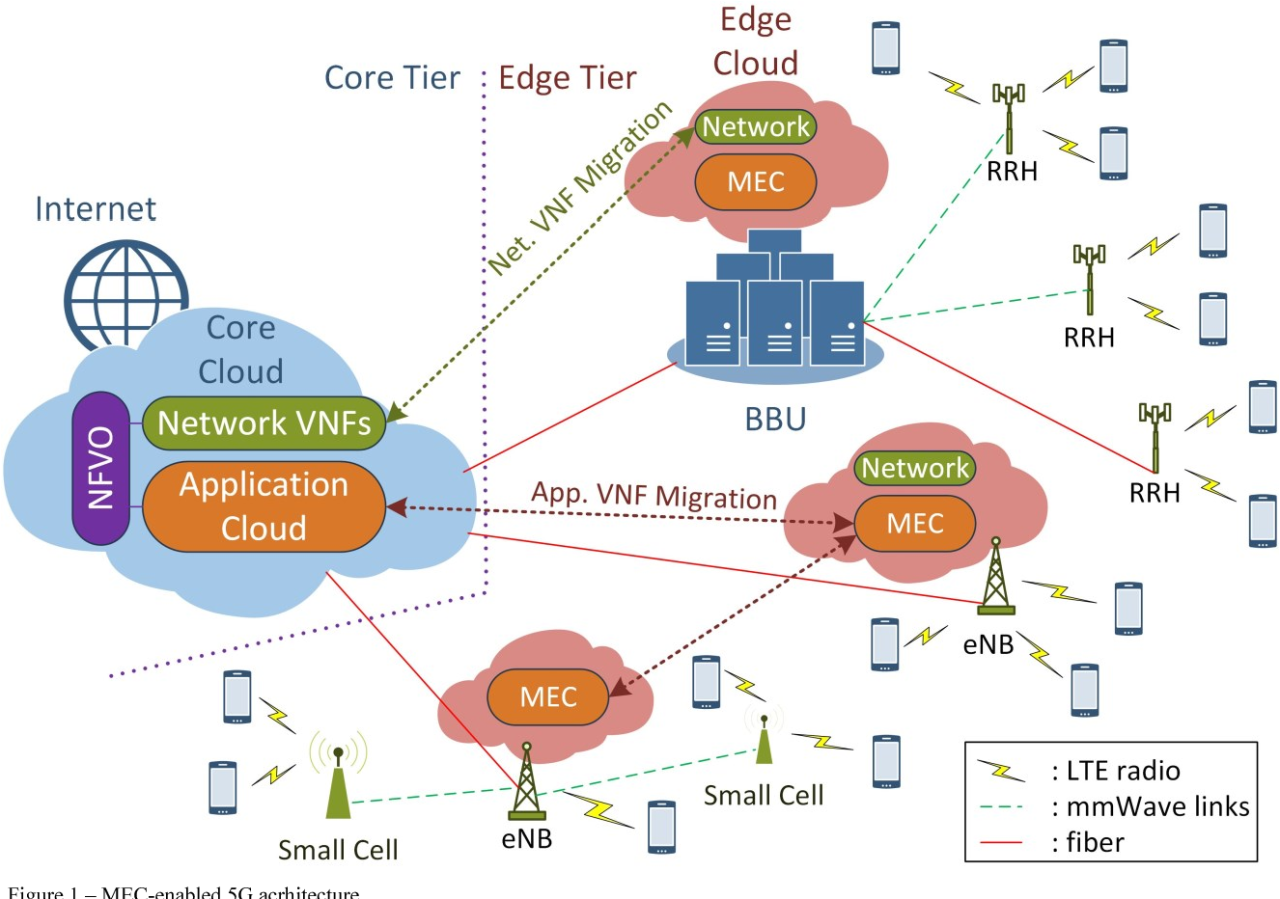
Cloud networking with 5G integration and traditional networking are two distinct approaches to network design and operation. Each approach has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice for a particular organization will depend on its specific needs and requirements.
- Key Features:Cloud networking with 5G integration leverages the cloud to provide network services, while traditional networking relies on physical network infrastructure.
- Benefits:Cloud networking with 5G integration offers benefits such as increased flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. Traditional networking provides benefits such as reliability and security.
- Challenges:Cloud networking with 5G integration faces challenges such as latency and security concerns. Traditional networking faces challenges such as inflexibility and scalability limitations.
The implications of these differences for network design and operation are significant. Cloud networking with 5G integration requires a different approach to network design and management than traditional networking. Traditional networking requires a more centralized approach, while cloud networking with 5G integration requires a more distributed approach.The
potential impact of 5G integration on the cloud networking market is significant. 5G integration is expected to drive the growth of the cloud networking market, as it will enable new applications and services that require high bandwidth and low latency.Key
trends and drivers shaping the future of cloud networking with 5G integration include:
- The increasing adoption of 5G networks
- The growing demand for cloud-based applications and services
- The need for increased network flexibility and scalability
Enterprises and service providers can prepare for and leverage the benefits of cloud networking with 5G integration by:
- Developing a clear understanding of the benefits and challenges of cloud networking with 5G integration
- Developing a strategy for migrating to cloud networking with 5G integration
- Partnering with a cloud networking provider that can provide the necessary expertise and support
Case Study: Cloud Networking with 5G Integration in a Smart City
In the smart city of Anytown, cloud networking with 5G integration has transformed urban infrastructure and enhanced the quality of life for its citizens. The seamless integration of cloud computing and 5G technology has created a robust and intelligent network that supports a wide range of smart city applications.
The implementation of this technology in Anytown faced several challenges. One major hurdle was the need to upgrade the existing network infrastructure to support 5G connectivity. Additionally, ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive data transmitted over the network was paramount.
Benefits
- Enhanced connectivity and reduced latency
- Increased bandwidth for data-intensive applications
- Improved efficiency and automation of city services
- Enhanced public safety and emergency response
- Empowerment of citizens through access to real-time information and services
Lessons Learned
- The importance of thorough planning and collaboration between stakeholders
- The need for robust security measures to protect sensitive data
- The value of involving citizens in the design and implementation process
- The potential for cloud networking with 5G integration to transform other aspects of urban life
Closing Notes
In conclusion, cloud networking with 5G integration is a game-changer that is redefining the landscape of connectivity. By embracing this transformative technology, organizations can unlock new levels of efficiency, innovation, and customer satisfaction. As we continue to witness the evolution of this technology, we can expect even more exciting developments that will shape the future of our digital world.