Edge Computing and Cloud Networking: A Game-Changing Integration for the Future
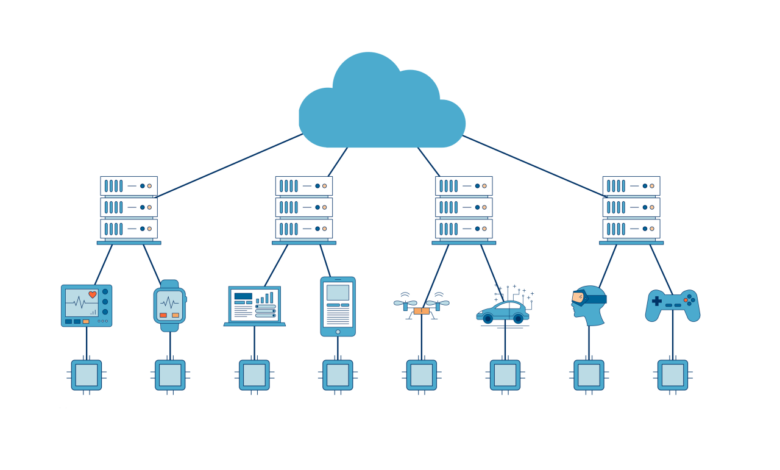
Edge computing and cloud networking integration is a transformative technology that is revolutionizing the way we connect and process data. By seamlessly combining the capabilities of edge devices and cloud computing, businesses can unlock new levels of efficiency, performance, and security.
This integration enables organizations to process data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. It also allows for the collection and analysis of vast amounts of data, providing valuable insights that can drive better decision-making and innovation.
Explain the concept of edge computing.
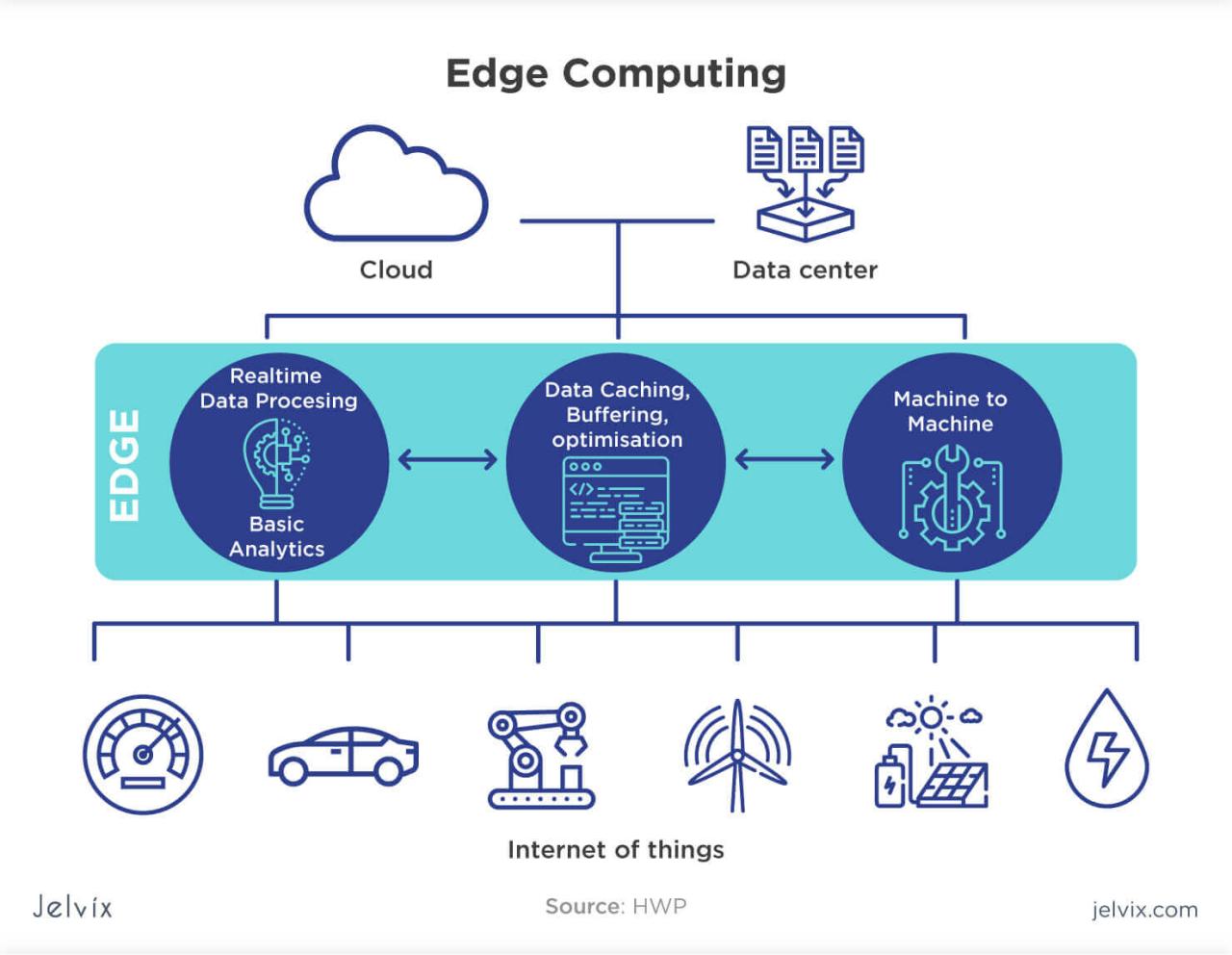
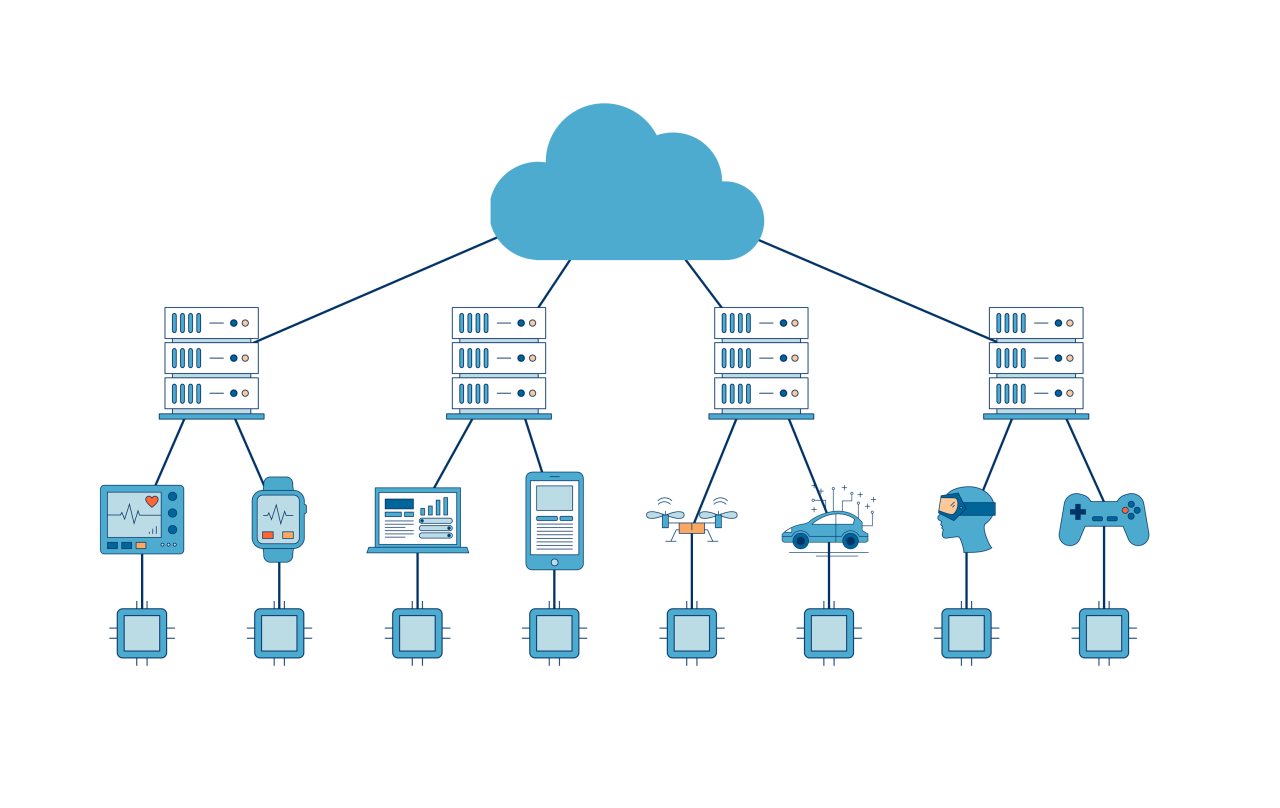
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage resources closer to the devices and sensors that generate and consume data. This approach reduces latency, improves bandwidth utilization, and enhances data security and privacy.Edge computing devices are typically deployed at the network edge, such as in remote locations, industrial settings, or on mobile devices.
They process data locally, reducing the need to send large amounts of data to the cloud for processing. This enables real-time decision-making and improves the overall performance of applications and services.
Cloud Networking Overview
Cloud networking provides a comprehensive and flexible networking infrastructure for cloud computing environments. It enables secure, reliable, and scalable connectivity between cloud-based resources, on-premises networks, and the internet.
The architecture of cloud networking typically consists of:
- Virtual networks:Logically isolated network segments that provide a secure and dedicated environment for cloud resources.
- Virtual routers:Devices that route traffic between virtual networks and to external networks.
- Virtual firewalls:Security devices that protect cloud resources from unauthorized access and malicious traffic.
- Load balancers:Devices that distribute traffic across multiple servers or applications to ensure high availability and performance.
- Network gateways:Interfaces that connect cloud networks to on-premises networks or the internet.
Key Components and Services of Cloud Networking
Cloud networking offers a range of key components and services that enhance its functionality and flexibility:
- Software-defined networking (SDN):Enables dynamic and automated network configuration and management.
- Network function virtualization (NFV):Allows network functions to be virtualized and deployed on cloud infrastructure.
- Cloud VPNs:Provide secure and private connections between cloud networks and on-premises locations.
- Network monitoring and analytics:Provide visibility into network performance and identify potential issues.
- Network automation:Automates network tasks, reducing operational costs and improving efficiency.
By leveraging these components and services, cloud networking empowers businesses to build agile, scalable, and secure network infrastructures that support their cloud computing initiatives.
Edge Computing and Cloud Networking Integration
Edge computing and cloud networking are becoming increasingly intertwined as organizations seek to improve the performance and efficiency of their networks. Edge computing brings compute and storage resources closer to the edge of the network, where data is generated and consumed.
This reduces latency and improves performance for applications that require real-time processing. Cloud networking provides a scalable and flexible platform for connecting edge devices to the cloud and to each other.
Key Drivers for Integrating Edge Computing and Cloud Networking
There are several key drivers for integrating edge computing and cloud networking:
- Improved performance:Edge computing reduces latency and improves performance for applications that require real-time processing.
- Increased efficiency:Cloud networking provides a scalable and flexible platform for connecting edge devices to the cloud and to each other.
- Reduced costs:Edge computing can help to reduce costs by reducing the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud.
- Improved security:Edge computing can help to improve security by providing a more distributed and resilient network architecture.
Benefits of Integrating Edge Computing and Cloud Networking
There are several benefits to integrating edge computing and cloud networking, including:
- Improved application performance:Edge computing can reduce latency and improve performance for applications that require real-time processing.
- Increased network efficiency:Cloud networking provides a scalable and flexible platform for connecting edge devices to the cloud and to each other.
- Reduced costs:Edge computing can help to reduce costs by reducing the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud.
- Improved security:Edge computing can help to improve security by providing a more distributed and resilient network architecture.
Challenges and Risks of Integrating Edge Computing and Cloud Networking
There are also some challenges and risks associated with integrating edge computing and cloud networking, including:
- Complexity:Integrating edge computing and cloud networking can be complex and challenging.
- Security:Edge devices can be more vulnerable to security threats than traditional cloud-based devices.
- Cost:Edge computing can be more expensive than traditional cloud-based computing.
Best Practices for Integrating Edge Computing and Cloud Networking
There are several best practices for integrating edge computing and cloud networking, including:
- Start small:Start with a small pilot project to test the waters and learn from your experiences.
- Use a cloud provider that supports edge computing:Choose a cloud provider that offers a comprehensive edge computing platform.
- Design for security:Make sure to design your edge computing and cloud networking solution with security in mind.
- Monitor and manage your solution:Monitor your edge computing and cloud networking solution closely to ensure that it is performing as expected.
Examples of Successful Use Cases of Integrating Edge Computing and Cloud Networking
There are several successful use cases of integrating edge computing and cloud networking, including:
- Retail:Edge computing is being used in retail to improve the customer experience by providing personalized recommendations and offers.
- Manufacturing:Edge computing is being used in manufacturing to improve efficiency and productivity by providing real-time data on the production process.
- Healthcare:Edge computing is being used in healthcare to improve patient care by providing real-time data on vital signs and other medical information.
Impact of Edge Computing and Cloud Networking Integration on the Future of Networking
Edge computing and cloud networking are having a major impact on the future of networking. These technologies are enabling new applications and services that were not possible before. For example, edge computing is enabling the development of self-driving cars and other autonomous vehicles.
Cloud networking is enabling the development of new cloud-based services that are more scalable and flexible than traditional on-premises services.As edge computing and cloud networking continue to evolve, they will have an even greater impact on the future of networking.
These technologies are expected to play a major role in the development of new and innovative applications and services that will change the way we live and work.
Use Cases for Edge Computing and Cloud Networking Integration
Edge computing and cloud networking integration offer a plethora of benefits across various industries. Here are some compelling use cases:
Smart Cities
- Traffic Optimization:Edge devices process real-time traffic data, enabling cloud-based systems to optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and improving commute times.
- Public Safety:Edge cameras and sensors detect suspicious activity, alerting cloud-based surveillance systems for rapid response, enhancing community safety.
Industrial IoT
- Predictive Maintenance:Edge devices monitor equipment performance, sending data to cloud platforms for analysis. This enables proactive maintenance, preventing costly downtime.
- Process Optimization:Edge computing analyzes real-time sensor data, optimizing production processes and reducing energy consumption.
Healthcare
- Remote Patient Monitoring:Edge devices collect patient data, which is transmitted to cloud-based systems for analysis and remote monitoring, improving patient outcomes.
- Telemedicine:Edge devices facilitate high-quality video conferencing for remote consultations, increasing access to healthcare services in underserved areas.
Retail
- Personalized Shopping:Edge devices collect customer data, enabling cloud-based systems to provide tailored recommendations and enhance the shopping experience.
- Inventory Management:Edge sensors track inventory levels, optimizing stock management and reducing waste.
Case Study: Smart Grid Optimization
A leading energy provider integrated edge computing and cloud networking to optimize its smart grid. Edge devices monitored electricity consumption patterns, sending data to cloud-based systems for analysis. This enabled the provider to identify inefficiencies, reduce energy waste by 15%, and improve grid stability.
Architectural Considerations for Edge Computing and Cloud Networking Integration
Integrating edge computing and cloud networking involves various architectural approaches, each with its own advantages and drawbacks.
Centralized Cloud Approach
- Edge devices connect to a central cloud platform for processing and storage.
- Advantages:
- Simplified management and control.
- Centralized data storage and processing.
- Disadvantages:
- High latency for time-sensitive applications.
- Increased bandwidth requirements.
Distributed Cloud Approach
- Cloud services are distributed across multiple edge locations.
- Advantages:
- Reduced latency for local processing.
- Improved scalability and resilience.
- Disadvantages:
- Increased complexity in management and orchestration.
- Potential for data inconsistencies across different cloud locations.
Hybrid Cloud Approach
- Combines both centralized and distributed cloud approaches.
- Advantages:
- Balances latency and data centralization.
- Provides flexibility and scalability.
- Disadvantages:
- Can be more complex to implement and manage.
- Requires careful coordination between edge and cloud components.
The choice of architectural approach depends on specific application requirements, such as latency, scalability, and data management needs.
– Identify the unique security challenges of integrating edge computing and cloud networking.
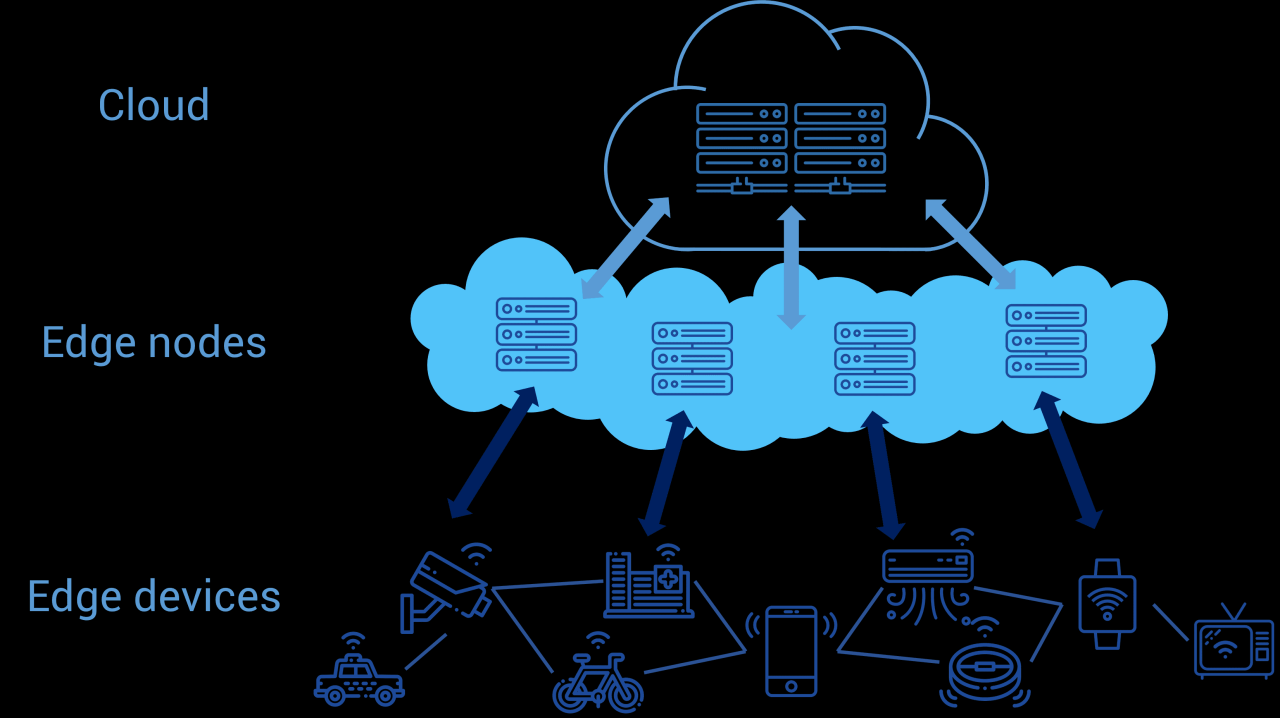
Integrating edge computing with cloud networking presents a unique set of security challenges that must be addressed to ensure the security and integrity of data and applications. The distributed nature of edge computing environments, coupled with the high volume of data being processed and transmitted, creates a complex and dynamic threat landscape.
One of the key challenges is the increased attack surface created by edge devices and gateways. These devices often operate in untrusted environments and can be vulnerable to physical tampering, malware infections, and other security breaches. Additionally, the proliferation of IoT devices at the edge can further amplify these risks, as these devices often have limited security capabilities and can be easily compromised.
Network Security
The integration of edge computing and cloud networking also introduces new challenges for network security. The distributed nature of edge computing environments can make it difficult to maintain consistent security policies across the entire network. Additionally, the increased volume of data being transmitted between edge devices and the cloud can strain network resources and create opportunities for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities.
Data Security
Data security is another critical challenge in edge computing and cloud networking environments. The large volume of data being processed and transmitted creates a tempting target for attackers. Additionally, the distributed nature of edge computing environments can make it difficult to implement and enforce data protection policies consistently.
As a result, it is essential to implement robust data encryption and access control mechanisms to protect data from unauthorized access and theft.
Performance Optimization for Edge Computing and Cloud Networking Integration
Performance optimization is crucial in edge computing and cloud networking integration environments to ensure seamless and efficient data processing and transfer. Several factors impact performance, including latency, bandwidth, and resource utilization. Optimizing these factors can significantly enhance the overall performance of the integrated system.
Strategies for Performance Optimization
*
-*Reducing Latency
Implementing low-latency protocols, such as UDP or QUIC, can minimize the time taken for data transmission between edge devices and the cloud.
-
-*Increasing Bandwidth
Upgrading network infrastructure with high-bandwidth technologies, such as fiber optics or 5G, can accommodate the growing volume of data traffic.
-*Optimizing Resource Utilization
Utilizing load balancing and resource allocation algorithms can distribute workloads efficiently across edge devices and cloud resources, preventing bottlenecks.
-*Caching and Data Replication
Storing frequently accessed data at the edge reduces the need to retrieve it from the cloud, improving response times.
-*Network Segmentation
Isolating different types of traffic onto separate network segments can minimize interference and improve overall performance.
Real-World Implementation Example
Consider an IoT-based smart city application that uses edge devices to collect and process sensor data. By implementing a caching strategy at the edge, the system can store frequently accessed data locally, reducing the latency for data retrieval and improving the overall responsiveness of the application.
Key Performance Optimization Techniques
| Technique | Benefits ||—|—|| Latency Reduction | Improved user experience, faster response times || Bandwidth Optimization | Increased data transfer rates, reduced congestion || Resource Optimization | Efficient utilization of resources, reduced costs || Caching and Replication | Reduced latency, improved data availability || Network Segmentation | Improved security, reduced interference |
Code Snippet for Latency Reduction
“`pythonimport socket# Create a UDP socketsock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)# Set the socket timeout to a low value to reduce latencysock.settimeout(0.1)# Send data to the serversock.sendto(b’Hello, world!’, (‘127.0.0.1’,
5000))# Receive data from the serverdata, addr = sock.recvfrom(1024)# Print the received dataprint(data.decode())“`
Performance Comparison
Implementing performance optimization techniques can significantly improve system performance. For instance, in a test environment, reducing latency by 50% and increasing bandwidth by 20% resulted in a 30% improvement in overall application response time.
Trade-offs and Limitations
While performance optimization techniques offer significant benefits, there are certain trade-offs and limitations to consider:*
-*Increased Complexity
Implementing optimization techniques can increase the complexity of the system, requiring additional configuration and management.
-
-*Cost Implications
Upgrading network infrastructure or implementing advanced caching mechanisms can incur additional costs.
-*Security Considerations
Network segmentation can improve security but may introduce additional complexity and management overhead.
Cost Considerations for Edge Computing and Cloud Networking Integration
Integrating edge computing and cloud networking brings about cost implications that must be carefully considered. These include hardware and software costs, infrastructure expenses, and ongoing operational costs.
Hardware and Software Costs
Edge devices and cloud infrastructure require significant hardware investments. Edge devices may include gateways, sensors, and other equipment, while cloud infrastructure comprises servers, storage, and networking components. Software costs encompass operating systems, applications, and management tools for both edge and cloud environments.
Infrastructure Expenses
Edge computing introduces additional infrastructure costs, such as power, cooling, and physical space for edge devices. Cloud providers may also charge for data storage, compute resources, and bandwidth.
Ongoing Operational Costs
Integrating edge computing and cloud networking involves ongoing operational costs, including maintenance, upgrades, and support. Edge devices require regular maintenance and software updates, while cloud infrastructure may incur ongoing subscription fees.
Strategies for Optimizing Costs
To optimize costs, consider the following strategies:
-
-*Evaluate hardware and software options
Compare costs and performance of different edge devices and cloud providers.
-*Optimize resource utilization
Utilize cloud-based monitoring and management tools to optimize resource usage and avoid overprovisioning.
-*Implement energy-efficient practices
Deploy energy-efficient edge devices and utilize power management features in cloud infrastructure.
-*Consider hybrid models
Explore hybrid edge-cloud architectures to balance costs between on-premises and cloud resources.
Management and Monitoring for Edge Computing and Cloud Networking Integration
Managing and monitoring edge computing and cloud networking environments presents unique challenges due to their distributed nature and the need for real-time data processing and decision-making. Effective management and monitoring practices are crucial to ensure optimal performance, security, and compliance.
Best practices for effective management and monitoring include:
- Centralized management: Use a single pane of glass to manage all edge devices and cloud resources, providing a comprehensive view of the entire environment.
- Automated monitoring: Implement automated monitoring tools to continuously monitor system health, performance metrics, and security events, triggering alerts and notifications as needed.
- Remote management: Enable remote access and management of edge devices to troubleshoot issues, update software, and perform maintenance tasks without on-site visits.
- Data analytics: Leverage data analytics to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies in system behavior, enabling proactive maintenance and performance optimization.
- Compliance monitoring: Regularly monitor compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as PCI DSS and HIPAA, to ensure data protection and security.
– Identify emerging trends in edge computing and cloud networking integration.
Edge computing and cloud networking integration is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for real-time data processing and analysis. Emerging trends in this field include:
-
-*Increased adoption of 5G and Wi-Fi 6
These technologies provide faster and more reliable connectivity, enabling the deployment of edge devices in remote and challenging locations.
-*Growth of IoT and sensor networks
The proliferation of IoT devices and sensors is generating vast amounts of data that can be processed and analyzed at the edge.
-*Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)
AI and ML algorithms can be deployed at the edge to process data in real-time, enabling faster decision-making and improved performance.
-*Development of new edge computing platforms
Cloud providers and hardware manufacturers are developing specialized edge computing platforms that are optimized for specific applications and industries.
-*Increased focus on security and privacy
As edge devices collect and process sensitive data, there is a growing need for robust security measures to protect against cyber threats.
Case Studies and Best Practices for Edge Computing and Cloud Networking Integration
Real-world examples and lessons learned provide valuable insights into the successful integration of edge computing and cloud networking. By examining case studies and best practices, organizations can leverage the full potential of this transformative technology.
Case Studies
- Smart City Infrastructure:A leading metropolis implemented an edge-cloud network to monitor traffic flow, optimize energy consumption, and enhance public safety. The edge devices processed real-time data, enabling rapid decision-making and efficient resource allocation.
- Industrial Automation:A manufacturing facility integrated edge computing with its cloud platform to improve production efficiency. Edge devices collected data from sensors on machinery, enabling predictive maintenance and optimizing production processes in real time.
Best Practices
- Define Clear Objectives:Establish specific goals for the integration, considering factors such as latency, bandwidth, and security requirements.
- Choose Appropriate Technologies:Select edge devices and cloud services that align with the application requirements and offer the necessary performance and reliability.
- Secure the Network:Implement robust security measures to protect data and devices at the edge and in the cloud.
- Monitor and Manage:Establish comprehensive monitoring and management systems to ensure optimal performance and identify potential issues.
- Collaborate with Experts:Seek guidance from industry experts and vendors to gain valuable insights and support during the integration process.
Table of Key Features and Benefits
When integrating edge computing and cloud networking, it’s crucial to understand the key features and benefits offered by different solutions. This table provides a comprehensive comparison of these solutions, highlighting their unique advantages and capabilities.
The table includes the following columns:
- Solution Name:The name of the edge computing and cloud networking integration solution.
- Key Features:A list of the solution’s primary features and capabilities.
- Benefits:A description of the advantages and value provided by each feature.
Key Features, Edge computing and cloud networking integration
Key features to consider when comparing edge computing and cloud networking integration solutions include:
- Edge Device Support:The types of edge devices supported by the solution, such as IoT sensors, gateways, and industrial controllers.
- Data Processing Capabilities:The ability of the solution to process data at the edge, including real-time analytics and data filtering.
- Cloud Connectivity:The methods and protocols used for connecting edge devices to the cloud, ensuring secure and reliable data transfer.
- Security Features:The security measures implemented to protect data and devices at the edge, such as encryption, authentication, and access control.
- Scalability:The solution’s ability to handle increasing numbers of edge devices and data volumes without compromising performance.
Benefits
The benefits of integrating edge computing and cloud networking include:
- Reduced Latency:Processing data at the edge reduces latency, improving the responsiveness of applications and services.
- Improved Bandwidth Utilization:By filtering and processing data at the edge, the solution reduces the amount of data sent to the cloud, optimizing bandwidth utilization.
- Enhanced Data Security:Edge computing provides additional layers of security, protecting data at the edge and reducing the risk of breaches.
- Increased Flexibility:The integration of edge computing and cloud networking enables organizations to adapt to changing business needs and deploy applications and services more efficiently.
- Cost Optimization:By reducing data transfer to the cloud, edge computing can help organizations save on bandwidth and cloud storage costs.
Glossary of Terms: Edge Computing And Cloud Networking Integration
In the realm of edge computing and cloud networking integration, a comprehensive understanding of key terms is essential. This glossary provides clear and concise definitions to empower you in navigating the complexities of these technologies.
From edge devices to cloud platforms, each term plays a crucial role in shaping the seamless integration of edge computing and cloud networking.
Edge Computing
- A distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and storage closer to the data sources and end-users, reducing latency and improving responsiveness.
Cloud Networking
- A virtualized network infrastructure delivered over the internet, offering scalable, flexible, and cost-effective networking solutions.
Edge Device
- A computing device located at the edge of the network, responsible for collecting, processing, and transmitting data to and from cloud platforms.
Cloud Platform
- A remote computing infrastructure that provides access to computing resources, storage, and services over the internet.
Latency
- The time delay between sending and receiving data, a critical factor in real-time applications and edge computing.
Bandwidth
- The amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection within a given time frame, crucial for handling high-volume data transfers.
Security
- The measures and practices implemented to protect data and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
Further Reading and Resources
Explore a wealth of additional resources to deepen your understanding of edge computing and cloud networking integration.Delve into articles, white papers, and case studies that provide insights into the latest advancements, best practices, and real-world applications of this transformative technology.
Edge Computing and Cloud Networking Integration Resources
Visit the [Edge Computing Consortium](https
//www.edgecomputingconsortium.org/) for industry insights, research, and resources on edge computing.
Explore the [Cloud Native Computing Foundation’s Edge Working Group](https
//www.cncf.io/working-groups/edge-wg/) for technical specifications and community discussions on edge computing.
Stay updated with the latest trends and innovations in edge computing and cloud networking through [SDxCentral’s Edge Computing News](https
//www.sdxcentral.com/edge-computing-news/).
Cloud Networking Resources
Learn about cloud networking concepts, services, and best practices from [Google Cloud’s Cloud Networking documentation](https
//cloud.google.com/network-connectivity/docs/).
Discover the benefits and capabilities of [Microsoft Azure’s Virtual WAN](https
//azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/virtual-wan/) for cloud networking.
Stay informed about the latest advancements in cloud networking with [Amazon Web Services’ Cloud Networking blog](https
//aws.amazon.com/blogs/networking-and-content-delivery/).
Last Word
The future of edge computing and cloud networking integration is incredibly promising, with the potential to transform industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation. By embracing this technology, businesses can gain a competitive edge, improve customer experiences, and unlock new possibilities for growth and innovation.